本文使用Dify v1.4.0版本,使用qwen-vl-max-latest作为多模态大模型。主要介绍了Dify工作流中的LLM节点的_invoke_llm方法的执行流程。
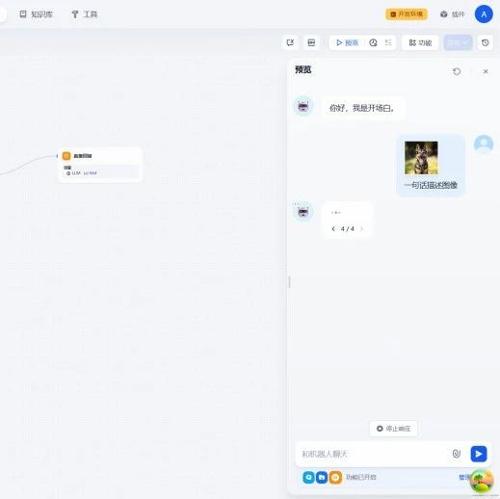
一.Chatflow流程示例
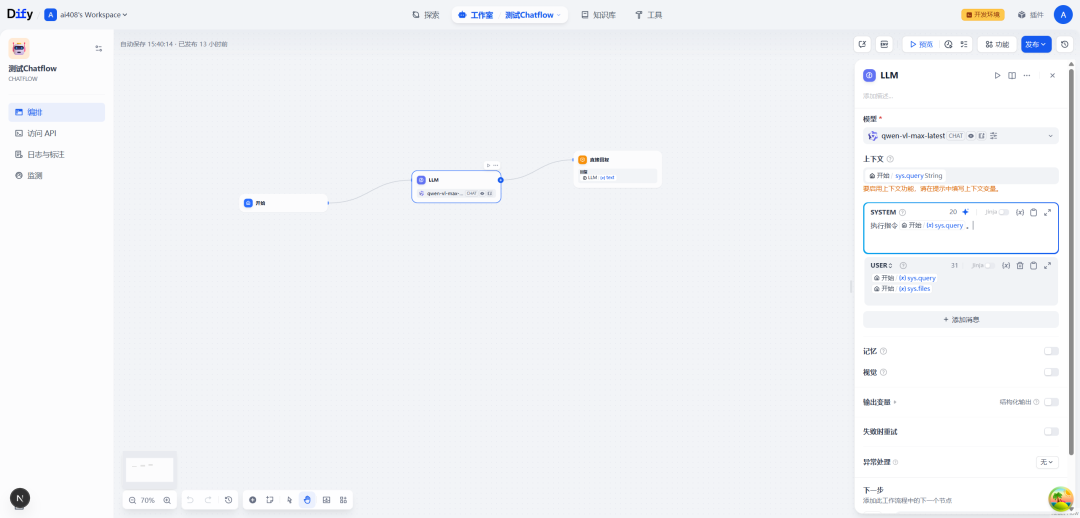
SYSTEM:
执行指令{{#sys.query#}}。
USER:
{{#sys.query#}}
{{#sys.files#}}
比如,用户在对话的时候,上传了一张图像,并且配上文字:一句话描述图像
二._invoke_llm函数
源码位置:dify\api\core\workflow\nodes\llm\node.py
该函数是 LLMNode 类中的核心方法,负责实际调用大语言模型并处理返回结果。函数返回一个生成器(Generator),允许流式处理模型响应。
def_invoke_llm(
self,
node_data_model: ModelConfig,
model_instance: ModelInstance,
prompt_messages: Sequence[PromptMessage],
stop: Optional[Sequence[str]] = None,
) -> Generator[NodeEvent, None, None]:
db.session.close()
invoke_result = model_instance.invoke_llm(
prompt_messages=list(prompt_messages),
model_parameters=node_data_model.completion_params,
stop=list(stop or []),
stream=True,
user=self.user_id,
)
return self._handle_invoke_result(invoke_result=invoke_result)
1.参数接收
-
node_data_model:包含模型名称、提供商和完成参数的配置 -
model_instance:已初始化的模型实例 -
prompt_messages:需要发送给模型的提示消息序列 -
stop:可选的停止词序列,用于控制模型生成
2.关闭数据库连接
这一步很关键,因为LLM调用通常耗时较长,关闭数据库会话可以释放资源,避免连接长时间占用。
db.session.close()
3.调用模型
invoke_result = model_instance.invoke_llm(...)
使用model_instance调用模型,关键参数包括:
-
将提示消息转换为列表
-
传入完成参数(
temperature、top_p等) -
设置停止词
-
启用流式响应(
stream=True) -
传入用户标识
4.处理结果
将模型返回的结果传递给_handle_invoke_result函数处理,该函数会将原始响应转换为工作流可以处理的事件流。
return self._handle_invoke_result(invoke_result=invoke_result)
三.invoke_llm函数
源码位置:dify\api\core\model_manager.py
invoke_llm方法是ModelInstance 类中用于调用大型语言模型的核心函数。
definvoke_llm(
self,
prompt_messages: Sequence[PromptMessage],
model_parameters: Optional[dict] = None,
tools: Sequence[PromptMessageTool] | None = None,
stop: Optional[Sequence[str]] = None,
stream: bool = True,
user: Optional[str] = None,
callbacks: Optional[list[Callback]] = None,
) -> Union[LLMResult, Generator]:
"""
Invoke large language model
:param prompt_messages: prompt messages
:param model_parameters: model parameters
:param tools: tools for tool calling
:param stop: stop words
:param stream: is stream response
:param user: unique user id
:param callbacks: callbacks
:return: full response or stream response chunk generator result
"""
ifnot isinstance(self.model_type_instance, LargeLanguageModel):
raise Exception("Model type instance is not LargeLanguageModel")
self.model_type_instance = cast(LargeLanguageModel, self.model_type_instance)
return cast(
Union[LLMResult, Generator],
self._round_robin_invoke(
function=self.model_type_instance.invoke,
model=self.model,
credentials=self.credentials,
prompt_messages=prompt_messages,
model_parameters=model_parameters,
tools=tools,
stop=stop,
stream=stream,
user=user,
callbacks=callbacks,
),
)
1. 参数验证与准备
-
接收多种参数:提示消息(
prompt_messages)、模型参数、工具列表、停止词等 -
根据
stream参数(默认为True)决定返回流式响应还是完整响应
2. 类型安全检查
ifnot isinstance(self.model_type_instance, LargeLanguageModel):
raise Exception("Model type instance is not LargeLanguageModel")
-
验证当前模型实例是否为大语言模型类型
-
使用
cast()进行类型标注,帮助类型检查器理解变量类型
3. 调用底层模型
通过_round_robin_invoke方法调用实际模型:
self._round_robin_invoke(
function=self.model_type_instance.invoke,
model=self.model,
credentials=self.credentials,
# 其他参数...
)
4. 负载均衡处理
_round_robin_invoke方法处理:
-
如果存在负载均衡管理器,使用轮询策略选择模型配置
-
尝试调用模型,处理可能发生的异常:
-
速率限制错误 – 冷却60秒并重试另一配置
-
认证/连接错误 – 冷却10秒并重试另一配置
5. 结果处理与返回
根据stream参数返回不同类型的结果:
-
True:返回生成器对象(Generator) -
False:返回完整响应(LLMResult)
这个函数通过轮询机制和异常处理实现了高可用性和负载均衡的模型调用功能。
四._round_robin_invoke函数
源码位置:dify\api\core\model_manager.py
这个函数实现了一个带有错误处理和负载均衡的函数调用机制。
def_round_robin_invoke(self, function: Callable[..., Any], *args, **kwargs) -> Any:
"""
Round-robin invoke
:param function: function to invoke
:param args: function args
:param kwargs: function kwargs
:return:
"""
ifnot self.load_balancing_manager:
return function(*args, **kwargs)
last_exception: Union[InvokeRateLimitError, InvokeAuthorizationError, InvokeConnectionError, None] = None
whileTrue:
lb_config = self.load_balancing_manager.fetch_next()
ifnot lb_config:
ifnot last_exception:
raise ProviderTokenNotInitError("Model credentials is not initialized.")
else:
raise last_exception
try:
if"credentials"in kwargs:
del kwargs["credentials"]
return function(*args, **kwargs, credentials=lb_config.credentials)
except InvokeRateLimitError as e:
# expire in 60 seconds
self.load_balancing_manager.cooldown(lb_config, expire=60)
last_exception = e
continue
except (InvokeAuthorizationError, InvokeConnectionError) as e:
# expire in 10 seconds
self.load_balancing_manager.cooldown(lb_config, expire=10)
last_exception = e
continue
except Exception as e:
raise e
1. 基础检查
-
首先检查是否存在负载均衡管理器(
load_balancing_manager) -
如果不存在,直接调用原始函数并返回结果
2. 错误处理准备
-
初始化
last_exception变量,用于记录最近一次捕获的异常 -
此变量可能是速率限制、授权或连接错误中的一种
3. 主循环逻辑
-
进入无限循环,不断尝试获取可用的配置并调用函数
-
通过
fetch_next()获取下一个负载均衡配置(lb_config) -
如果没有可用配置:
-
无异常记录时抛出
ProviderTokenNotInitError -
有异常记录时重新抛出该异常
4. 函数调用尝试
-
从
kwargs中移除可能存在的credentials参数 -
使用配置中的凭证调用目标函数
-
成功执行则直接返回结果
5. 异常处理策略
-
捕获到速率限制错误(
InvokeRateLimitError): -
将当前配置冷却60秒
-
记录异常并继续循环尝试下一个配置
-
捕获到授权或连接错误(
InvokeAuthorizationError,InvokeConnectionError): -
将当前配置冷却10秒
-
记录异常并继续循环尝试下一个配置
-
捕获到其它异常:
-
直接向上抛出异常,终止执行
这种设计允许系统在遇到临时性错误(如速率限制)时自动尝试其它可用配置,提高了系统的可靠性和容错能力。
五._handle_invoke_result
源码位置:dify\api\core\workflow\nodes\llm\node.py
这个函数处理 LLM 调用的结果,无论是阻塞模式还是流式模式,并将结果转换为工作流节点事件。此函数是工作流 LLM 节点处理结果的核心部分,确保了 LLM 生成的内容能够正确地转换为工作流事件。
def_handle_invoke_result(
self, invoke_result: LLMResult | Generator[LLMResultChunk, None, None]
) -> Generator[NodeEvent, None, None]:
# For blocking mode
if isinstance(invoke_result, LLMResult):
event = self._handle_blocking_result(invoke_result=invoke_result)
yield event
return
# For streaming mode
model = ""
prompt_messages: list[PromptMessage] = []
usage = LLMUsage.empty_usage()
finish_reason = None
full_text_buffer = io.StringIO()
for result in invoke_result:
contents = result.delta.message.content
for text_part in self._save_multimodal_output_and_convert_result_to_markdown(contents):
full_text_buffer.write(text_part)
yield RunStreamChunkEvent(chunk_content=text_part, from_variable_selector=[self.node_id, "text"])
# Update the whole metadata
ifnot model and result.model:
model = result.model
if len(prompt_messages) == 0:
# TODO(QuantumGhost): it seems that this update has no visable effect.
# What's the purpose of the line below?
prompt_messages = list(result.prompt_messages)
if usage.prompt_tokens == 0and result.delta.usage:
usage = result.delta.usage
if finish_reason isNoneand result.delta.finish_reason:
finish_reason = result.delta.finish_reason
yield ModelInvokeCompletedEvent(text=full_text_buffer.getvalue(), usage=usage, finish_reason=finish_reason)
1.函数入口
-
接收
invoke_result参数,类型可以是LLMResult(阻塞模式)或Generator[LLMResultChunk, None, None](流式模式) -
返回
Generator[NodeEvent, None, None]类型的生成器
2.阻塞模式处理
-
检查
invoke_result是否为LLMResult类型 -
调用
_handle_blocking_result处理结果并生成单个事件 -
生成事件后立即返回
3.流式模式处理
初始化变量:
4.处理流式结果
遍历每个 result:
5.生成完成事件
-
循环结束后,生成
ModelInvokeCompletedEvent事件 -
该事件包含累积的完整文本、使用情况统计和完成原因
参考文献
[0] Dify工作流中的LLM节点:_invoke_llm方法:https://z0yrmerhgi8.feishu.cn/wiki/ZmN7w2jzriXcs7ksXjFc0H1Pnwg
[1] https://github.com/langgenius/dify/releases/tag/1.4.0
知识星球服务内容:Dify源码剖析及答疑,Dify对话系统源码,NLP电子书籍报告下载,公众号所有付费资料。加微信buxingtianxia21进NLP工程化资料群。
(文:NLP工程化)