

为什么要做 xVerify?
当前推理模型( Reasoning Model)在多个领域取得了显著进展,但在长推理链、 困难数学表达式、多语言等复杂场景下,答案抽取与验证仍面临以下挑战:
-
慢思考场景:长推理链包含阶段性结果和自我反思等过程,识别和判断其正确性较为复杂。
-
表达多样性:复杂数学表达(LaTeX / 分数 / 自然语言)、多语言描述的答案等价性判断比较困难。
-
评估局限性:基于规则的工具(如 Math-Verify)缺乏灵活性,而基于 LLM 的评估模型则缺乏针对性的训练。
为了解决这些问题,上海算法创新研究院的研究团队推出了 xVerify ——首个针对长推理链回答、覆盖多种题型、支持中英文双语的高效答案验证工具。相比 Hugging Face 官方组件 Math-Verify,xVerify 支持的题型更广、验证方式更全面、准确率更高,多数场景下的评估准确率可达 96% 以上。

项目仓库:
https://github.com/IAAR-Shanghai/xVerify
Hugging Face论文链接:
https://huggingface.co/papers/2504.10481
xVerify 模型开源仓库:
https://huggingface.co/collections/IAAR-Shanghai/xverify-67e0f6f94c2dc334727da802
arXiv论文链接:
https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.10481
xVerify 具有以下特点和优势:
面向推理模型,有效处理长推理链。xVerify 的训练集中采样了多个推理模型在高难度数据集上生成的长推理链回答,针对性地强化了 xVerify 处理长推理链回答的能力。因而,xVerify 可以有效处理推理模型回答中的阶段性结果和自我反思部分对于其最终答案正确性判断的干扰。
广泛适用,支持多种题型。xVerify 适用于多种评测场景,支持数学题、选择题、分类任务和简答题。其具备强大的等价判断能力,能精准识别不同题型的等价答案,主要支持中文和英文,并兼容其他语言。
智能答案识别,精准匹配等价表达。xVerify 不仅可自动处理字母大小写转换(如 a -> A)、希腊字母(如 alpha -> α)等基础变化,还能识别数学表达式的多种等价形式,如 LaTeX(45\frac{4}{5}54 -> 4/5)、科学计数法(1.34 × 10³ -> 13400)及自然语言(one hundred and twenty-three -> 123)。
并且针对复高难度数学题进行训练,可以有效应对复杂数学表达式的等价性判断。即使 LaTeX 表达式不完整或格式不同,xVerify 也能正确解析。此外,在简答题场景下,xVerify 可判断大模型生成的答案是否与正确答案在内容上对齐。
多种模型变体,可供灵活选择。xVerify 提供了多个不同种类和参数规模型的模型,基座模型包括 Qwen 2.5、Gemma 2、LLaMA 3.1/3.2、GLM 4、Phi-4 等,参数规模涵盖 0.5B 到 32B,从而有效减少基础模型的偏差。用户可以根据计算资源和具体评测需求选择最合适的模型,以确保评测的效率和准确性。

xVerify 的构建流程
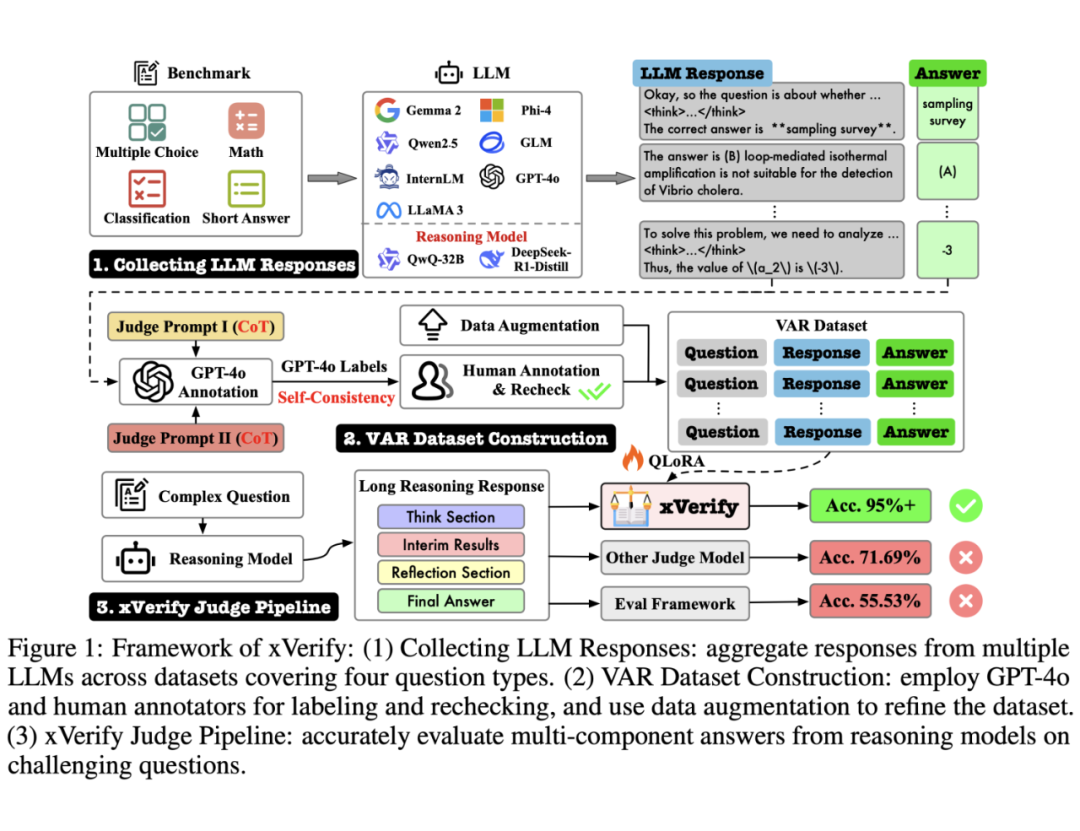
📌 第一阶段:VAR 数据集构建
该研究系统性地整理了 20 余个权威 benchmark 数据集,包括 AIME 2024、LiveMathBench、GPQA、MATH、GSM8K 等,涵盖多种高难度数学推理任务和不同答案表达形式。
基于这些数据,他们在近 20 种基座模型(包含多个推理模型)上,设计多样化的提示策略,生成包含复杂推理过程与多样化答案形式的问答数据。
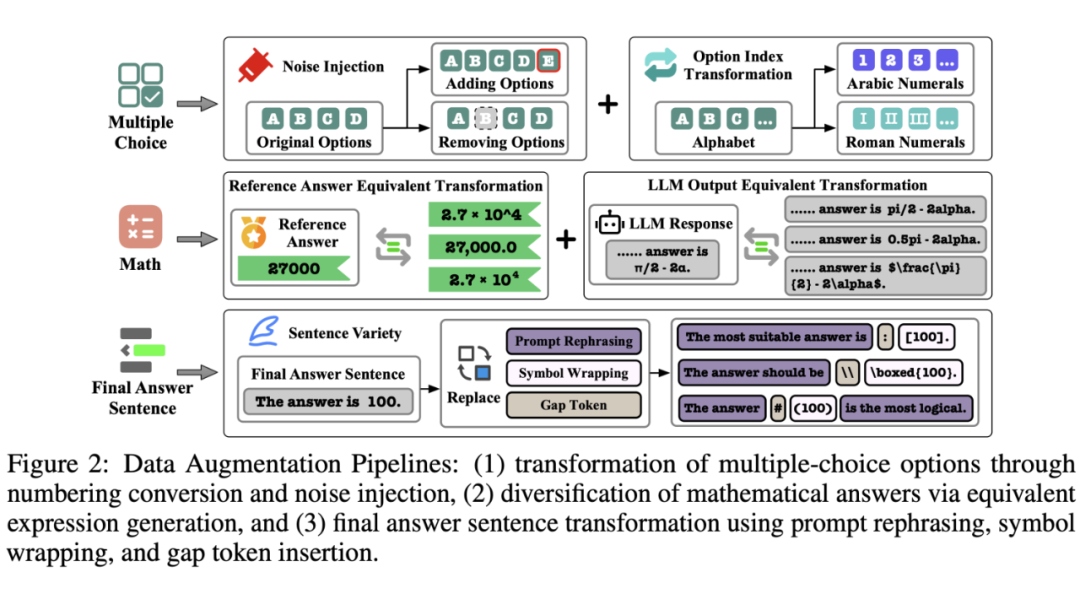
为了增强模型的跨场景泛化能力,他们特别在数据划分时确保训练集与泛化集覆盖不同的 benchmark 来源及 LLM,并设计了多种不同的数据增强策略来多样化已有的大模型问答样本(见下图),从而评估 xVerify 是否能适应多样化的真实评估场景,而不仅仅依赖特定的训练数据模式。
在数据标注过程中,该团队采用 GPT-4o 和人工标注团队对对训练集和测试集进行多轮标注和复核,以确保标注的准确性和一致性。具体而言,他们首先使用 GPT-4o 基于不同的提示词进行两轮自动标注,针对标注结果中存在分歧或涉及复杂数学表达的样本进行人工复核。
针对测试集和泛化集,他们采取更严格的质量控制措施,所有数据均由人工再次标注,以确保其作为高质量评估基准,能够准确衡量模型的有效性和泛化能力。
最终,基于精心设计的数据收集、回答生成、数据划分以及标注策略,该团队最终构建了 Verify Answer for Reasoning (VAR) 数据集,一个多样化、高质量的长推理链数据集。
VAR 数据集包含训练集(43204)、测试集(6122)和泛化集(6468),训练集和测试集用于训练和评估 xVerify 模型,而泛化集作为测试集的补充,用于检验 xVerify 在更多样化的评估场景中的泛化能力。
📌 第二阶段:模型训练
该研究基于 LLama-Factory 框架,在 VAR 数据集的训练集上针对多个模型进行微调,所使用的基座模型涵盖了不同的架构(如 Qwen2.5、Gemma2、Phi-4 系列)和参数规模(0.5B 至 32B)。
最终所有 xVerify 模型均展现出超过较高的高准确率,尤其在处理长推理链、数学表达式等价性判断等核心任务中表现显著优于传统方法。

实验对比
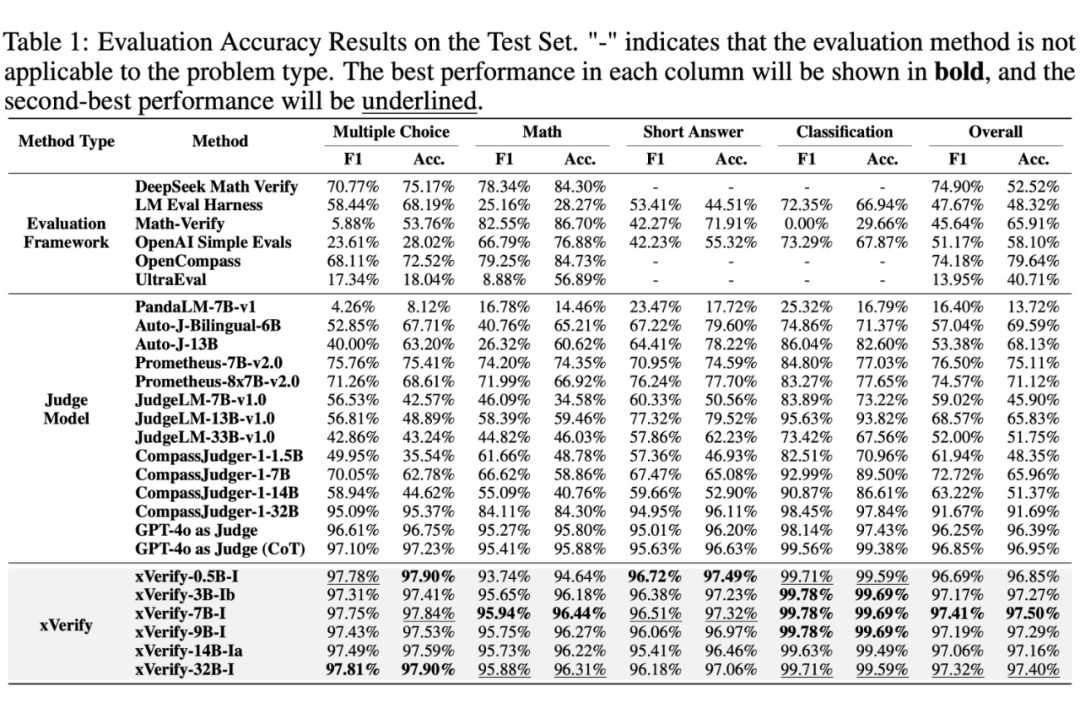
该研究通过四类题型(多选题、数学题、简答题、分类题)与主流评估方法(评估框架和 Judge Model)进行对比,结果显示,xVerify 在不同题型上的评估准确率均有显著优势,且具有良好的泛化性能。
即使是最小的 xVerify 模型( xVerify-0.5B-I),其表现仍然能全面超越除 GPT-4o 外的所有方法,而 xVerify-3B-Ib 则全面超越其他方法。
-
测试集评估结果
-
泛化集评估结果
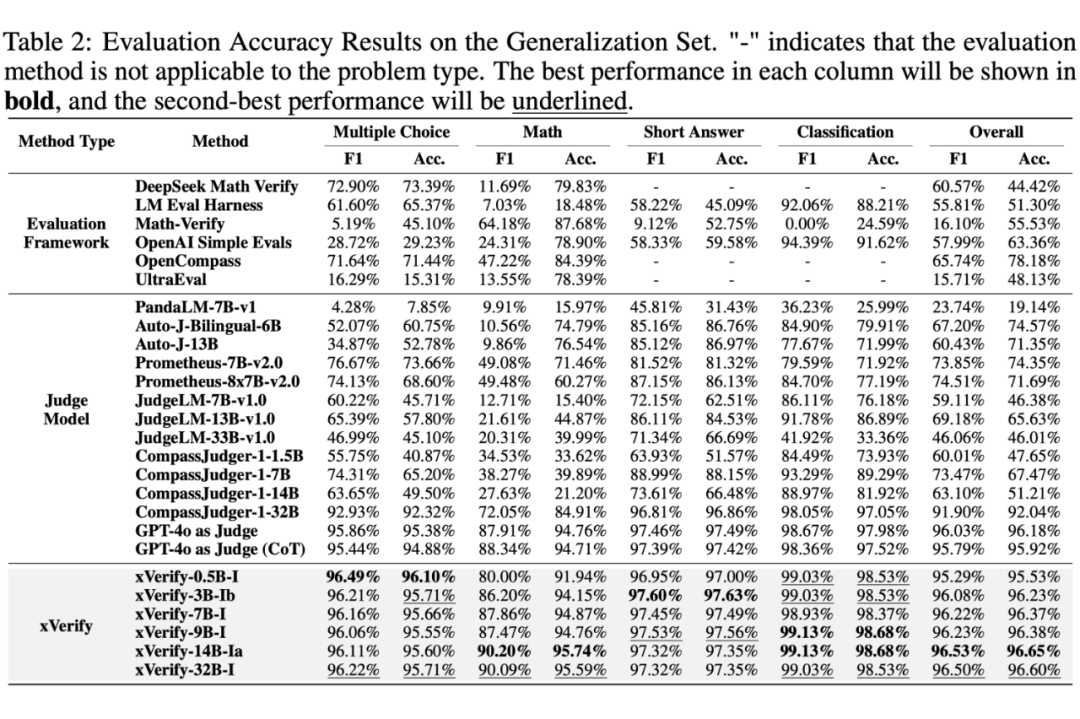
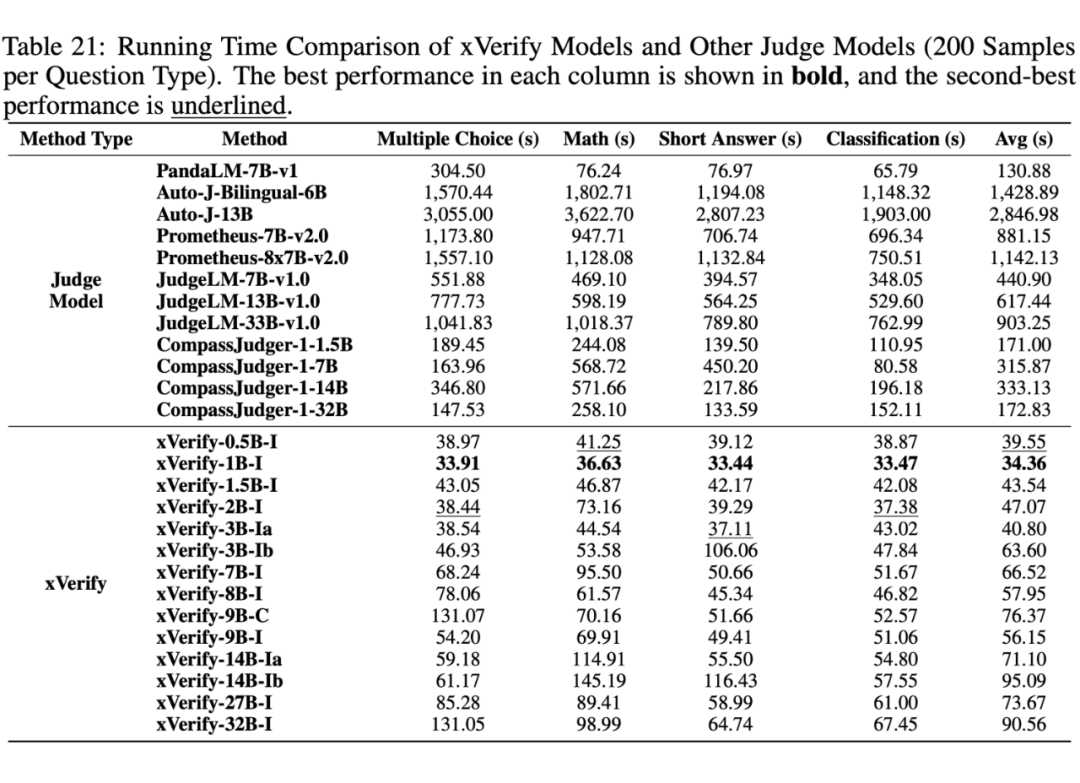
此外,论文附录中还提供了全部 14 个 xVerify 模型的完整评估结果,并针对对比了所有 judge model 和 xVerify 模型的评估效率,实验结果显示 xVerify 模型的推理效率显著优于其他模型。

xVerify 评估示例
● 数学题
{
"index": 1,
"question": "$已知函数f(x)=|x-a|+2|x+1|(a>0)。$\n$若a=3,求不等式 f(x)>5 的解集;$",
"correct_answer": "$(-\\infty ,-\\frac{4}{3})\\cup (0,+\\infty )$",
"llm_output": "\n首先,我们考虑函数 \\( f(x) = |x - 3| + 2|x + 1| \\) 在 \\( a = 3 \\) 时的形式。\n\n接下来,我们需要确定函数 \\( f(x) \\) 的分段形式。由于 \\( |x - 3| \\) 和 \\( |x + 1| \\) 都是绝对值函数,我们需要找到 \\( x \\) 的值,使得这些绝对值函数内部的表达式为零,即 \\( x = 3 \\) 和 \\( x = -1 \\)。\n\n因此,函数 \\( f(x) \\) 可以分为三个部分:\n\n1. 当 \\( x < -1 \\) 时,\\( f(x) = -(x - 3) + 2(-(x + 1)) = -x + 3 - 2x - 2 = -3x + 1 \\)。\n2. 当 \\( -1 \\leq x < 3 \\) 时,\\( f(x) = -(x - 3) + 2(x + 1) = -x + 3 + 2x + 2 = x + 5 \\)。\n3. 当 \\( x \\geq 3 \\) 时,\\( f(x) = (x - 3) + 2(x + 1) = x - 3 + 2x + 2 = 3x - 1 \\)。\n\n现在,我们要求解不等式 \\( f(x) > 5 \\)。\n\n- 对于 \\( x < -1 \\),不等式变为 \\( -3x + 1 > 5 \\),解得 \\( x < -\\frac{4}{3} \\)。\n- 对于 \\( -1 \\leq x < 3 \\),不等式变为 \\( x + 5 > 5 \\),解得 \\( x > 0 \\)。\n- 对于 \\( x \\geq 3 \\),不等式变为 \\( 3x - 1 > 5 \\),解得 \\( x > 2 \\)。\n\n将这些解集合并,我们得到 \\( x \\) 的解集为 \\( x < -\\frac{4}{3} \\) 或 \\( x > 0 \\)。\n\nThe answer is \\( x < -\\frac{4}{3} \\) 或 \\( x > 0 \\).",
"xVerify_judgment": "Correct"
},
{
"index": 2,
"question": "In each town in ARMLandia, the residents have formed groups, which meet each week to share math problems and enjoy each others' company over a potluck-style dinner. Each town resident belongs to exactly one group. Every week, each resident is required to make one dish and to bring it to his/her group.\n\nIt so happens that each resident knows how to make precisely two dishes. Moreover, no two residents of a town know how to make the same pair of dishes. Shown below are two example towns. In the left column are the names of the town's residents. Adjacent to each name is the list of dishes that the corresponding resident knows how to make.\n\n| ARMLton | |\n| :--- | :--- |\n| Resident | Dishes |\n| Paul | pie, turkey |\n| Arnold | pie, salad |\n| Kelly | salad, broth |\n\n\n| ARMLville | |\n| :--- | :--- |\n| Resident | Dishes |\n| Sally | steak, calzones |\n| Ross | calzones, pancakes |\n| David | steak, pancakes |\n\nThe population of a town $T$, denoted $\\operatorname{pop}(T)$, is the number of residents of $T$. Formally, the town itself is simply the set of its residents, denoted by $\\left\\{r_{1}, \\ldots, r_{\\mathrm{pop}(T)}\\right\\}$ unless otherwise specified. The set of dishes that the residents of $T$ collectively know how to make is denoted $\\operatorname{dish}(T)$. For example, in the town of ARMLton described above, pop(ARMLton) $=3$, and dish(ARMLton) $=$ \\{pie, turkey, salad, broth\\}.\n\nA town $T$ is called full if for every pair of dishes in $\\operatorname{dish}(T)$, there is exactly one resident in $T$ who knows how to make those two dishes. In the examples above, ARMLville is a full town, but ARMLton is not, because (for example) nobody in ARMLton knows how to make both turkey and salad.\n\nDenote by $\\mathcal{F}_{d}$ a full town in which collectively the residents know how to make $d$ dishes. That is, $\\left|\\operatorname{dish}\\left(\\mathcal{F}_{d}\\right)\\right|=d$.\nLet $n=\\operatorname{pop}\\left(\\mathcal{F}_{d}\\right)$. In terms of $n$, compute $d$.",
"correct_answer": "(1 + (1 + 8n)^(1/2)) / 2",
"llm_output": "To find the number of dishes $d$ in terms of the population $n$ of a full town $\mathcal{F}_{d}$, we need to understand how the residents of the town can make pairs of dishes.\n\nSince each resident knows how to make precisely two dishes, and no two residents of a town know how to make the same pair of dishes, we can think of each resident as a unique pair of dishes.\n\nIn a full town, for every pair of dishes in $\operatorname{dish}(T)$, there is exactly one resident in $T$ who knows how to make those two dishes. This means that each pair of dishes corresponds to exactly one resident.\n\nTherefore, the number of pairs of dishes is equal to the number of residents. The number of pairs of dishes can be calculated using the combination formula: $\binom{d}{2} = \frac{d(d-1)}{2}$.\n\nSince each resident corresponds to a unique pair of dishes, the number of residents is equal to the number of pairs of dishes: $n = \frac{d(d-1)}{2}$.\n\nWe can rearrange this equation to solve for $d$: $d^2 - d - 2n = 0$.\n\nUsing the quadratic formula, we can solve for $d$: $d = \frac{1 \pm \sqrt{1 + 8n}}{2}$.\n\nSince $d$ must be a positive integer, we take the positive root: $d = \frac{1 + \sqrt{1 + 8n}}{2}$.",
"xVerify_judgment": "Correct"
},
{
"index": 3,
"question": "Consider an $m$-by-$n$ grid of unit squares, indexed by $(i,j)$ with $1 \\leq i \\leq m$ and $1 \\leq j \\leq n$. There are $(m-1)(n-1)$ coins, which are initially placed in the squares $(i,j)$ with $1 \\leq i \\leq m-1$ and $1 \\leq j \\leq n-1$. If a coin occupies the square $(i,j)$ with $i \\leq m-1$ and $j \\leq n-1$ and the squares $(i+1,j), (i,j+1)$, and $(i+1,j+1)$ are unoccupied, then a legal move is to slide the coin from $(i,j)$ to $(i+1,j+1)$. How many distinct configurations of coins can be reached starting from the initial configuration by a (possibly empty) sequence of legal moves?",
"correct_answer": "$\\binom{m+n-2}{m-1}$",
"llm_output": "Here's how to solve this problem:\n\n**Understanding the Problem**\n\nWe have a grid where coins can move diagonally to empty spaces. The key is to realize that the coins effectively \"fill\" the grid in a specific way. \n\n**Key Observation**\n\n* A coin can only move to an empty square diagonally adjacent to it.\n* Once a coin is placed in a square, it cannot move back to its original position.\n\n**Solution Approach**\n\n1. **Final State:** Think about the final possible configurations. The coins will end up in a specific set of squares. \n\n2. **Constraints:** The constraints on the moves dictate that the coins will always form a pattern where they occupy the squares along a diagonal.\n\n3. **Counting Configurations:** The number of distinct configurations is determined by the number of ways to choose which squares along the diagonal will be occupied by coins.\n\n**Formalizing the Counting**\n\nLet's represent the grid with a sequence of 0s and 1s, where 1 represents a coin and 0 represents an empty square. Since the coins always move diagonally, the sequence will have a specific pattern. \n\nFor example, if *m* = 4 and *n* = 4, the initial configuration would be:\n\n```\n1111\n1000\n1000\n1000\n```\n\nAnd a possible final configuration could be:\n\n```\n1010\n0101\n0000\n0000\n```\n\nNotice that the final configuration has a diagonal pattern of 1s. The number of distinct configurations is determined by the number of ways to choose the positions of the 1s in this diagonal pattern.\n\n\n**The answer is <(m-1)(n-1)>.** \n\n\n\nLet me know if you'd like a more detailed explanation of why this is the case!",
"xVerify_judgment": "Incorrect"
},
{
"index": 4,
"question": "A cattle breeder owns 52 dairy cows. Each cow gives 1000 oz of milk per day. Calculate the amount of milk produced per week by the cows.",
"correct_answer": "$3.64 \\times 10^5",
"llm_output": "Let's calculate the total amount of milk produced per week by the cows.\n\n**Step 1: Determine the number of days in a week.**\n- A week has **7 days**.\n\n**Step 2: Calculate the total milk production per day.**\n- Number of cows = 52\n- Milk produced per cow per day = 1000 oz\n- **Total milk per day** = \\( 52 \\text{ cows} \\times 1000 \\text{ oz/day} = 52,000 \\text{ oz/day} \\)\n\n**Step 3: Calculate the total milk production per week.**\n- **Total milk per week** = \\( 52,000 \\text{ oz/day} \\times 7 \\text{ days} = 364,000 \\text{ oz} \\)\n\n**Final Answer:**\nThe total amount of milk produced per week by the cows is Three hundred sixty-four thousand.",
"xVerify_judgment": "Correct"
}● 简答题
{
"index": 5,
"question": "What is greater: the combined 2011 populations of Rennington (Northumberland), Lydbrook (Gloucestershire), Stow-on-the-Wold (Gloucestershire) and Witney (Oxfordshire), or the 2022 population of London?",
"correct_answer": "The 2022 population of London",
"llm_output": "To answer this question, we need to find the populations of the given locations and compare them to the population of London in 2022.\n\n1. Find the 2011 populations of Rennington (Northumberland), Lydbrook (Gloucestershire), Stow-on-the-Wold (Gloucestershire), and Witney (Oxfordshire).\n - Rennington (Northumberland): approximately 190 residents\n - Lydbrook (Gloucestershire): approximately 1,341 residents\n - Stow-on-the-Wold (Gloucestershire): approximately 3,555 residents\n - Witney (Oxfordshire): approximately 29,469 residents\n\n2. Calculate the combined population of these locations in 2011.\n - Combined population: 190 + 1341 + 3555 + 29469 = 37,355\n\n3. Find the 2022 population of London.\n - The 2022 population of London is approximately 9,000,000.\n\n4. Compare the combined population of the four locations to the population of London in 2022.\n - The population of London (approximately 9,000,000) is greater than the combined population of the four locations (approximately 37,355).\n\nThe answer is The population of London is greater.",
"xVerify_judgment": "Correct"
}● 选择题
{
"index": 6,
"question": "Identity refers to one's Answer Choices: (A) Use of a particular coping strategy (B) Control over one's own life story (C) Physical appearance and overall personality (D) Coherent sense of self",
"correct_answer": "D",
"llm_output": "The question asks about \"Identity,\" which is a complex concept related to how we perceive ourselves. \n\nLet's analyze the options:\n\n* **Use of a particular coping strategy:** This relates to how we deal with stress and challenges, not our sense of self.\n* **Control over one's own life story:** This touches on agency and self-determination, which are aspects of identity, but not the core definition.\n* **Physical appearance and overall personality:** These are external factors that can influence how we perceive ourselves, but they don't fully encompass the essence of identity.\n* **Coherent sense of self:** This is the most accurate answer. Identity is about having a clear understanding of who you are, your values, beliefs, and how you see yourself in the world.",
"xVerify_judgment": "Correct"
}● 分类题
{
"index": 7,
"question": "Where Is the Real Jayne Ann Krentz?: It was hard to believe that this novel was written by JAK. The prologue was the best part of the book. It started out with an explosion of character involvement and then the fire went out. She failed to give the reader a true insight into the main characters. I was hard pressed to understand why the two main characters were attracted to each other. I could only assume it was because they were trying to save a small company. There was no \"electricity\" between them. She had numerous secondary characters that never stood on their own. I read the entire book in one weekend, only because if I put the book down, I could not remember who was who. I hope the real JAK comes back to us soon.\nPlease identify the sentiment polarity of the sentence: positive or negative",
"correct_answer": "negative",
"llm_output": "To identify the sentiment polarity of the sentence, let's break it down:\n\n1. The reviewer states that it was \"hard to believe\" that the novel was written by JAK, implying that they were disappointed with the quality of the book.\n2. They mention that the prologue was the best part of the book, but this is a negative statement because it implies that the rest of the book was not as good.\n3. The reviewer criticizes the author for failing to give the reader a true insight into the main characters and for not making the characters' attraction to each other believable.\n4. They also mention that the secondary characters were not well-developed, which is another negative point.\n5. The reviewer states that they read the book in one weekend, but this is not a positive statement because it implies that they were trying to finish the book quickly rather than enjoying it.\n6. Finally, they express a hope that the \"real JAK\" will return, which implies that they are disappointed with the current quality of the author's work.\n\nOverall, the sentiment polarity of the sentence is negative.",
"xVerify_judgment": "Correct"
}
未来展望
xVerify 已经开源了完整评估代码(GitHub)和部分 xVerify 模型(Hugging Face),用户可直接调用进行评估任务。此外,该团队后续将近一步开源更多 xVerify 模型,并探索在针对推理模型的新应用场景中验证 xVerify 的有效性,同时欢迎关注 R1 模型复现、长推理评估的研究者与开发者使用和讨论。
(文:PaperWeekly)

